How to choose between timing belt drive and chain drive for circular guide conveyor line?
In circular guide conveyor line, timing belt drive and chain drive are two common transmission methods. The difference between the two is only in the transmission method. The structures of other parts are basically the same, but they have their own characteristics and are suitable for different scenarios and needs.
1. Timing belt drive:
Timing belt drive is a driving method that is easy to design and has cost-effective advantages. The servo motor drives the timing pulley to rotate, and the timing belt and the slide are connected by a slotted or clamped design.
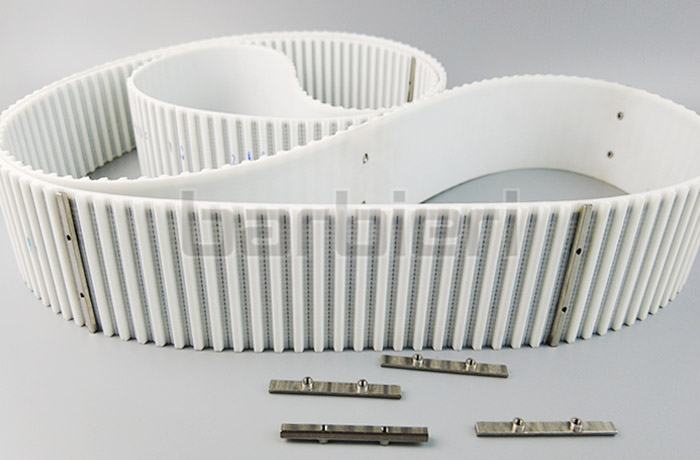
Timing belt drive is widely favored for its high speed, low noise and high precision. It is composed of polyurethane and steel wire, and realizes synchronous transmission without slip through precise tooth meshing. This transmission method is particularly suitable for occasions with high requirements for speed, precision and quiet performance. In addition, timing belt drive also has the advantages of easy maintenance and no lubrication, which further reduces the cost of use.
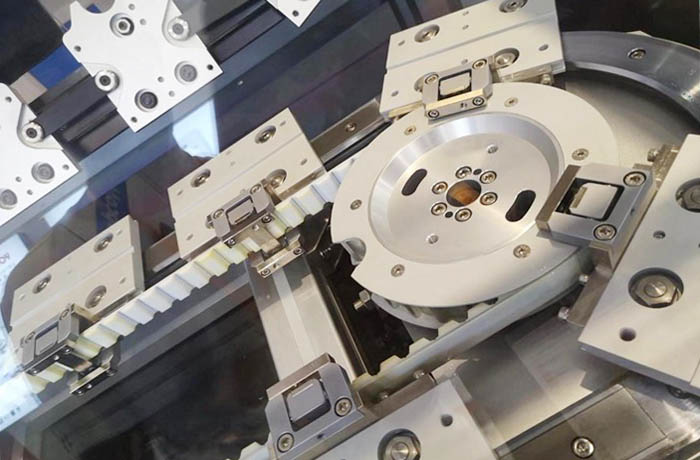
2. Chain drive
The slider and chain can be connected directly or through a transmission rod. Compared with the timing belt, the chain can withstand a larger load.
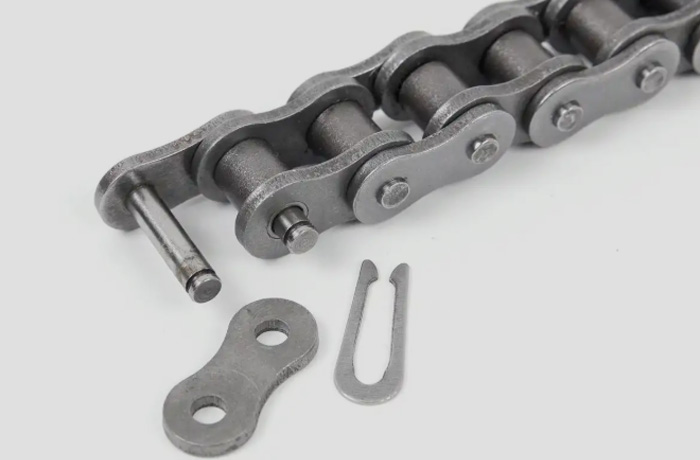

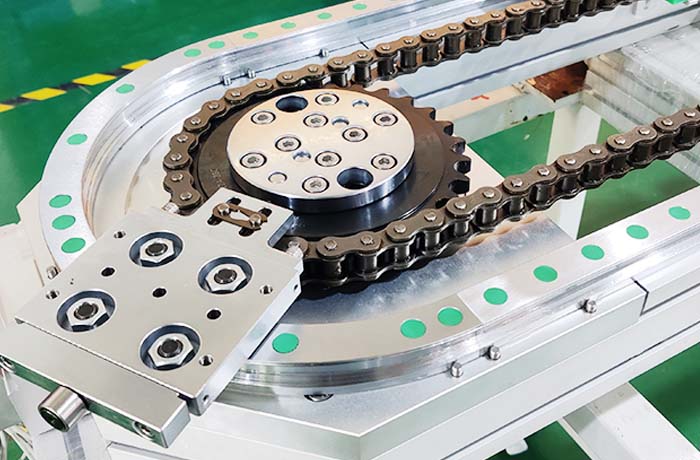
Chain drive is known for its heavy load, long line and high maintenance cost. It transmits power through the meshing of chain and sprocket, and has high load-bearing capacity and long service life. Chain drive shows its unique advantages in occasions where high power needs to be transmitted and the working environment is relatively harsh. However, it also requires regular lubrication and maintenance to ensure its normal operation and extend its service life.

Comparison of the core characteristics of timing belt drive and chain drive
Features | Timing belt drive | Chain drive |
Transmission principle | The belt teeth mesh with the pulley teeth, without relative sliding | The chain link meshes with the sprocket teeth, and there is a slight gap |
Load capacity | Medium (depending on the belt width/material) | High (heavy chain can carry several tons) |
Operating speed | High-speed adaptation, smooth and impact-free | Mostly medium and low speeds, high speed is prone to vibration |
Transmission accuracy | High | Relatively low |
Maintenance requirements | Low (lubrication-free, long life) | High (regular lubrication and tension adjustment are required) |
Noise level | Low (smooth meshing, no impact) | High (chain link and sprocket mesh with impact) |
Cleanliness | High (no oil pollution, suitable for dust-free environment) | Low (lubricating oil may pollute the environment) |
Environmental adaptability | Resistant to normal temperature and clean environment, afraid of high temperature (≤80℃), oil pollution | Resistant to high and low temperatures (-40~200℃), dust, oil pollution, and requires anti-corrosion treatment |
Lifespan | Short (affected by temperature and load, about 1-3 years) | Longer (5-10 years with proper maintenance) |
Summary
Synchronous belts are suitable for: light load, high speed, high precision, clean environment, low maintenance, low noise scenarios;
3C lithium battery, medical, photovoltaic new energy, automotive electronics and other industries;
Chains are suitable for: heavy load, low speed, harsh environment (high and low temperature/dust/corrosion), long life, high maintenance tolerance scenarios.
Heavy material handling, construction machinery assembly, foundry workshop, electroplating line, heat treatment process.




