Advantages of Timing Belt Drives in Circular Guideway Conveyor Lines
Timing belt used in circular guideway systems are specially processed. Their core function is to accurately, smoothly, and synchronously transmit power and motion along a closed, circular track. Whether in cleanroom environments or dusty, conventional industrial environments, timing belt drives in circular guideway conveyor lines are highly adaptable. Their non-slip, highly wear-resistant, and lubrication-free properties ensure stable performance under a variety of harsh operating conditions.
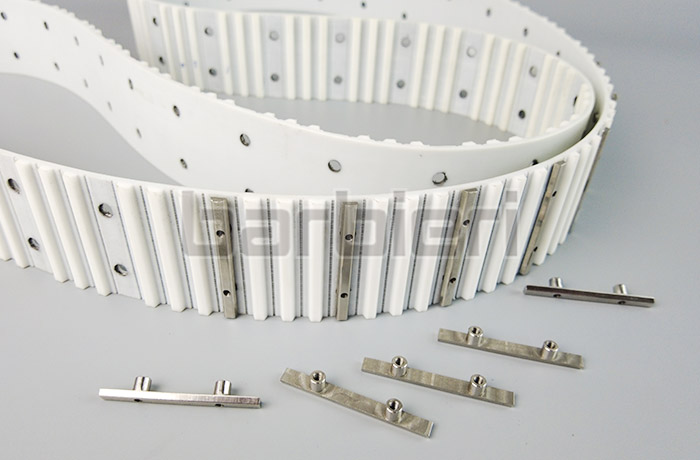
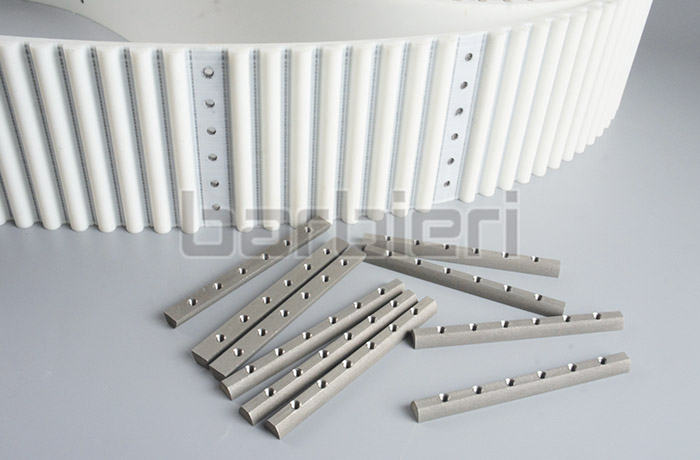


Core Functions of Timing Belt Circular Guideway Conveyor Lines:
Synchronous Drive: Timing belt teeth mesh with the timing pulleys to transmit power, eliminating slip and ensuring accurate and synchronous transmission of the drive unit's motion to the moving slide or worktable.
Circular Closure: Designed or connected as a loop, it perfectly matches the closed-loop shape of the circular guideway, enabling continuous, cyclical motion.
Smooth Drive: Provides continuous, pulsation-free motion transmission, smooth operation, and relatively low noise.
Positioning Transmission: In circular guideway systems, the timing belt is typically connected directly to the moving slide. Therefore, it not only transmits motion but also directly bears the force required to pull the load, precisely converting the motor's rotation into linear or precisely circular positioning of the slider along the guide rail.
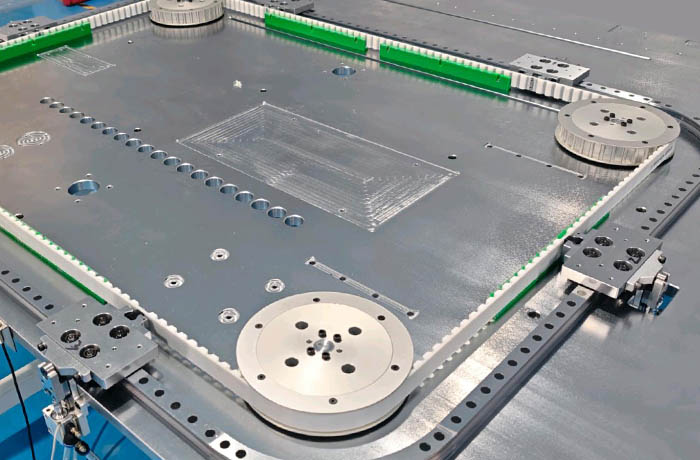
Advantages of using a timing belt for circular guides:
High Speed and Smoothness: Smooth operation with low vibration and noise makes it suitable for high-speed applications.
High-Precision Positioning: Compared to chains or rack and pinion systems, timing belts provide higher motion repeatability and lower transmission backlash.
Lightweight Design: Timing belt drive systems are generally more compact and lightweight than rack and pinion systems, reducing the overall weight of the equipment, alleviating the load on the drive system and improving equipment efficiency.
Low Maintenance Cost: Timing belts are wear-resistant and require no lubrication, resulting in cleaner operation. They rarely require the frequent lubrication of chains and gears, reducing maintenance.
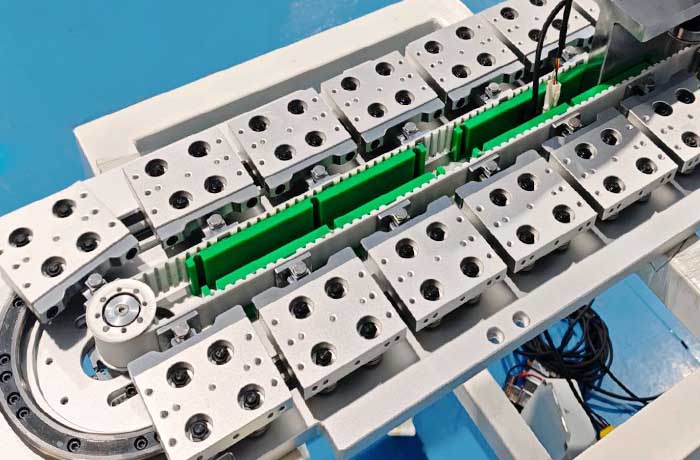
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Timing Belt (for Circular Guide Applications):
*Load Size and Type: Determine the required strength specifications of the timing belt.
*Speed and Acceleration: Determine the timing belt's tooth profile, material selection, and required minimum bend radius.
*The diameter of the endless guide rail must ensure that the selected timing belt can smoothly navigate the guide rail's minimum bend radius without excessive stress and wear. Circular toothed belts generally perform better with smaller bend radii.
*Drive type: Whether it is a single-point or multi-point drive, and the tensioning method should also be considered.
*Connection method: The strength and finish of the connection method (such as steel buckles or adhesive bonding) are critical. They must be smooth and durable to avoid affecting meshing and bending performance.
*Timing pulley: The timing belt's tooth profile must be precisely matched. Annular guide rails often use specially designed timing pulleys with flanges to guide the timing belt smoothly and prevent lateral movement.




